- Email: sales@flait-aluminum.com
- Tel: 0086-13203837398

For more detailed information including pricing, customization and shipping.
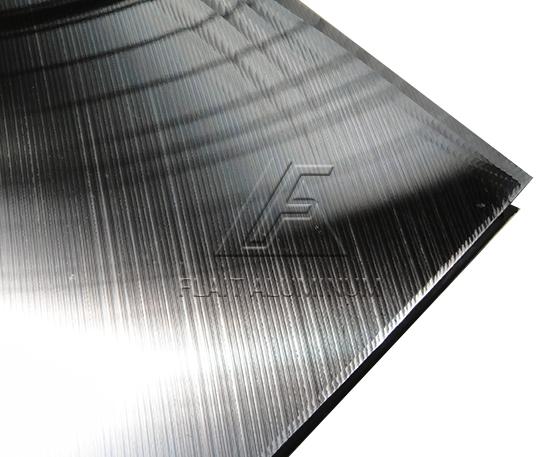
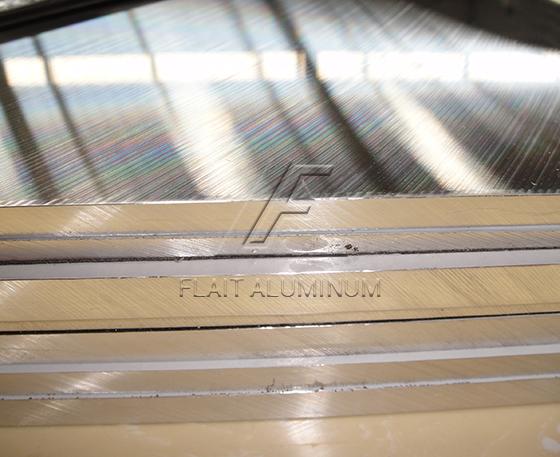



Precision ground 6061 aluminum plate is made from the 6061 aluminum alloy, which consists primarily of aluminum (Al) and magnesium (Mg).Precision grinding is a machining process that involves removing material from the surface of the aluminum plate using abrasive wheels. This process helps to achieve tight tolerances, excellent flatness, and a smooth surface finish.Precision ground 6061 aluminum plates are known for their exceptional flatness, meaning the plate has a uniform thickness across its entire surface. The surface finish is typically very smooth, providing a high-quality appearance.




|
Alloy |
6061 precision ground aluminum plate |
|
Temper |
T6,T651 |
|
Thickness(mm) |
0.3-600 |
|
Width(mm) |
500-2600 |
|
Thickness Tolerance |
±0.002 in |
|
Finish Type |
Precision Ground |
|
Application |
Semiconductor and Electronics, Aerospace,Precision Machinery,Tool and Mold Making,General Engineering,etc. |
|
Alloy |
Temper |
Mechanical Properties |
|||||
|
Tensile Strength, Ultimate(Mpa) |
Tensile Strength, Yield(Mpa) |
Elongation at Break |
Brinell hardness HBW |
Modulus of Elasticity(GPa) |
Shear Strength(Mpa) |
||
|
6061 |
T6,T651 |
290 |
255 |
12% |
95-100 |
68.9 |
186 |
 High Flatness: Precision grinding ensures a high degree of flatness, which is essential for applications requiring close dimensional control.
High Flatness: Precision grinding ensures a high degree of flatness, which is essential for applications requiring close dimensional control. Excellent Surface Finish: The smooth surface finish of precision ground 6061 aluminum plates makes them suitable for applications where aesthetics are important.
Excellent Surface Finish: The smooth surface finish of precision ground 6061 aluminum plates makes them suitable for applications where aesthetics are important. Machinability: 6061 aluminum alloy has good machinability, allowing for various machining operations on precision ground plates, such as drilling, milling, and tapping.
Machinability: 6061 aluminum alloy has good machinability, allowing for various machining operations on precision ground plates, such as drilling, milling, and tapping. Corrosion Resistance: Like other 6061 aluminum plates, precision ground versions offer good resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for outdoor and corrosive environments.
Corrosion Resistance: Like other 6061 aluminum plates, precision ground versions offer good resistance to corrosion, making them suitable for outdoor and corrosive environments. Semiconductor and Electronics: Used for precision components, fixtures, and tooling in the semiconductor and electronics industry.
Semiconductor and Electronics: Used for precision components, fixtures, and tooling in the semiconductor and electronics industry. Aerospace: Suitable for aircraft structural components, tooling, and fixtures that require high precision and flatness.
Aerospace: Suitable for aircraft structural components, tooling, and fixtures that require high precision and flatness. Precision Machinery: Used in precision instruments, jigs, and fixtures for industries such as metrology, optics, and robotics.
Precision Machinery: Used in precision instruments, jigs, and fixtures for industries such as metrology, optics, and robotics. Tool and Mold Making: Used for mold bases, tooling plates, and precision components in the tool and mold making industry.
Tool and Mold Making: Used for mold bases, tooling plates, and precision components in the tool and mold making industry. General Engineering: Suitable for various precision applications, such as mounting plates, optical benches, and inspection fixtures.
General Engineering: Suitable for various precision applications, such as mounting plates, optical benches, and inspection fixtures.